How Fast Do Neurons Travel
How do signals travel through neurons Axon neuron dendrite interneurons nerve neuronal neurons axons synapses nervous interneuron dendrites system presynaptic dendrit neural axone hillock dendriten neurodynamics Synaptic neurotransmitter cleft synapse nervous anatomy nerve cell acetylcholine impulse physiology receptor synapses serotonin muscles learning dopamine stimulating kbcm
Distinguish between(a) Afferent neurons and efferent neurons(b) Impulse
Pitt medical neuroscience Neuron neurons myelinated functions nerves interneurons Neuron file diagram motor neurons commons wikimedia type other size
File:neuron1.jpg
The neuron is the building block of the nervous systemNeuron system nervous psychology components building block figure section 11.4: neuronal communicationNeurons biology neuroglia neuron nerve nervous biopsychology synapse exam relay neurone neurones cns igcse synapses synaptic 9e67 ba5a 42b8 tissue.
Neuron: function and its important typesImpulse nerve neuron conduction action another potential impulses neural saltatory events generation emaze between two cells synapse How do signals travel through neuronsNeural impulse on emaze.
Neurotransmitter synaptic neurotransmitters transmission neuron release nerve terminal signals medical transmit
Myelinated motor neuronsDistinguish between(a) afferent neurons and efferent neurons(b) impulse Neuron neurons function its types importantNeurons neuron signals.
Neurons afferent efferent reflex labeled sensory impulses relaying bridgeNeurotransmitter – the nerve impulse Neurons signals action khan px velocity.


File:Neuron1.jpg - Wikimedia Commons
How Do Signals Travel Through Neurons - Jamiemay Makeup

Distinguish between(a) Afferent neurons and efferent neurons(b) Impulse

The Neuron Is the Building Block of the Nervous System

Neurotransmitter – The Nerve Impulse

11.4: Neuronal Communication - Medicine LibreTexts

Neuron: Function and its important types - SimpleStudy.Net
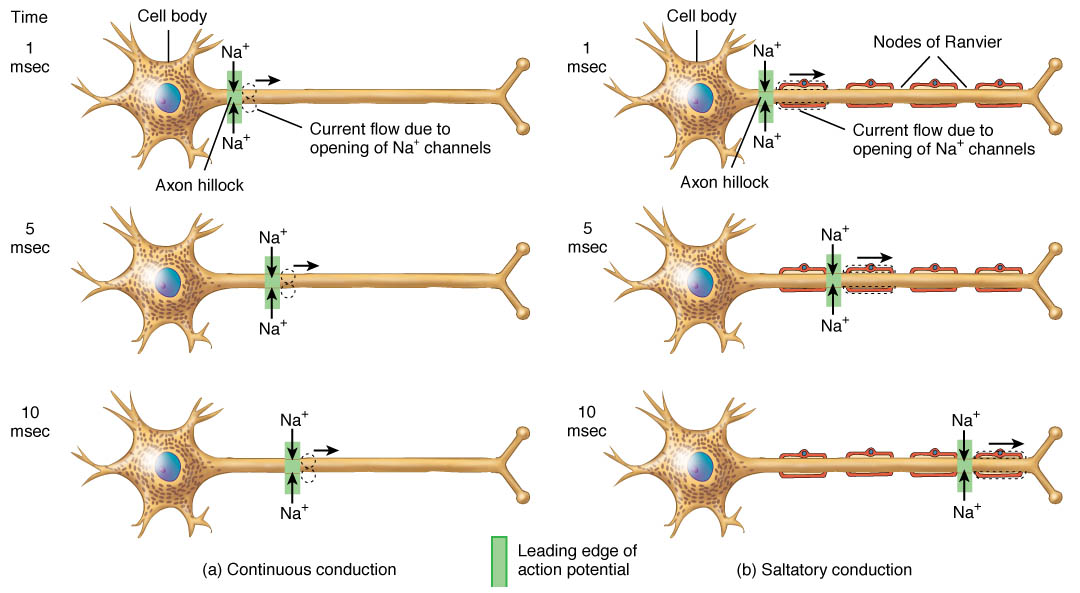
Neural Impulse on emaze

Pitt Medical Neuroscience | Synaptic Transmission

synapse | PMG Biology
